How Do Different Bonding Materials Affect the Performance of Cut Off Grinding Wheels?
 2025.08.22
2025.08.22
 Industry News
Industry News

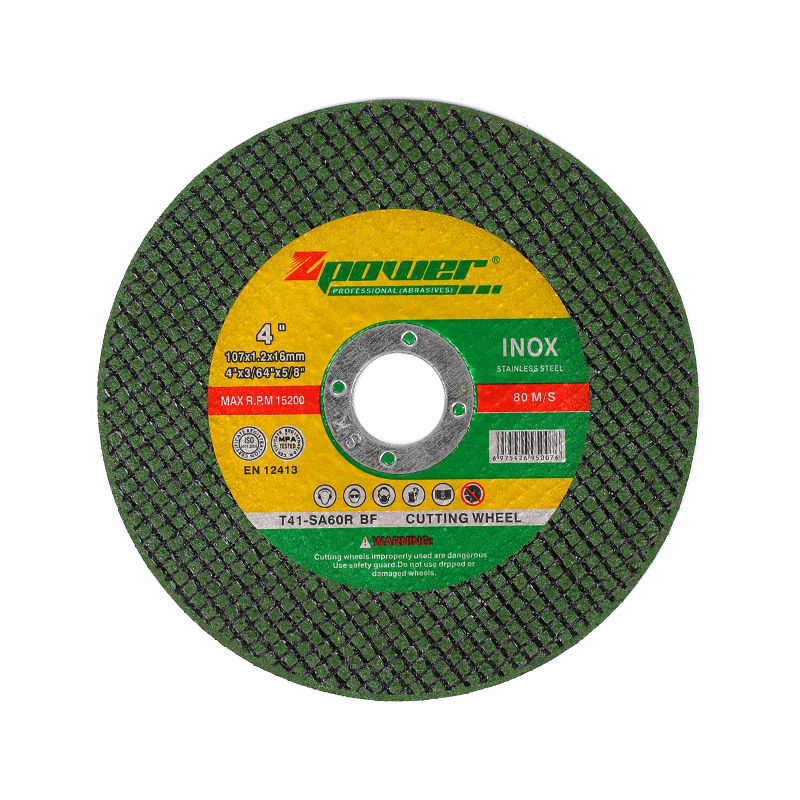
Cut off grinding wheels are widely used in metalworking and construction for cutting through a variety of materials. These wheels consist of abrasive grains held together by a bonding material, which plays a crucial role in determining the wheel’s performance and durability.
One common bonding material found in cut off grinding wheels is vitrified bond. This type of bond is made from a mixture of clays and ceramic materials that are fired at high temperatures to create a hard, glass-like structure. Vitrified bonds are known for their rigidity and strength, which allow the wheel to maintain its shape and cutting ability even under heavy use. Wheels with vitrified bonds often provide precise cuts and tend to wear evenly, which can contribute to a consistent finish on the workpiece. However, these bonds are also more brittle, making the wheels more susceptible to cracking or breaking if mishandled or used improperly.
Another widely used bonding material is resin bond, which consists of synthetic resins such as phenolic compounds. Resin bond wheels are generally more flexible and less brittle than vitrified wheels, which allows them to absorb vibrations and resist impacts better. This makes resin bonded cut off grinding wheels suitable for applications where some degree of flexibility is beneficial, such as in portable tools or in environments where the wheels may encounter sudden shocks. Resin bonds also tend to wear faster, which can be advantageous for aggressive cutting where the wheel needs to expose fresh abrasive grains frequently. On the downside, resin bonds are more sensitive to heat and may degrade faster if the wheel is overheated during use.
Rubber bonding is another type found in certain types of cut off wheels, especially those designed for specific industries or materials. Rubber bonds offer excellent shock absorption and flexibility, which reduces the risk of wheel damage and improves user comfort during prolonged use. Wheels with rubber bonding can be particularly useful for cutting softer metals or composites where a gentler touch is necessary. However, rubber bonded wheels may not be suitable for high-speed cutting or heavy-duty tasks because they may not retain abrasive grains as firmly under intense stress.
Metal bonding is also used in some specialized cut off grinding wheels, especially those intended for cutting very hard or abrasive materials. These wheels use metal powders as the bonding agent, which provide high strength and thermal conductivity. Metal bonded wheels tend to generate less heat during cutting and can last longer when used on tough surfaces like stone or ceramics. However, they are generally less flexible and require careful handling to prevent damage.
The choice of bonding material affects not only the durability and cutting efficiency of the cut off grinding wheels but also their safety during operation. For example, vitrified bonded wheels need to be handled with care to avoid cracks, and users must avoid dropping or striking these wheels. Resin bonded wheels require attention to temperature control to prevent overheating and premature wear. Understanding these characteristics helps operators select the right wheel and maintain it properly for safe use.
Performance can also be influenced by how the bonding material interacts with the abrasive grains. In some wheels, the bond is designed to wear away at a rate similar to the abrasive, exposing fresh grains and maintaining cutting effectiveness. In others, a stronger bond holds grains more firmly but may reduce cutting speed. The balance between bond strength and abrasive exposure is key to achieving efficient and reliable cutting with cut off grinding wheels.
The bonding material plays a significant role in determining the performance, durability, and safety of cut off grinding wheels. Vitrified, resin, rubber, and metal bonds each offer distinct advantages and limitations that make them suitable for different applications. By understanding these differences, users can make informed decisions when selecting grinding wheels and optimize their results while maintaining safe operating conditions. Proper care and attention to the bonding material can enhance the lifespan and effectiveness of cut off grinding wheels across various cutting tasks.

 Eng
Eng  عربى
عربى